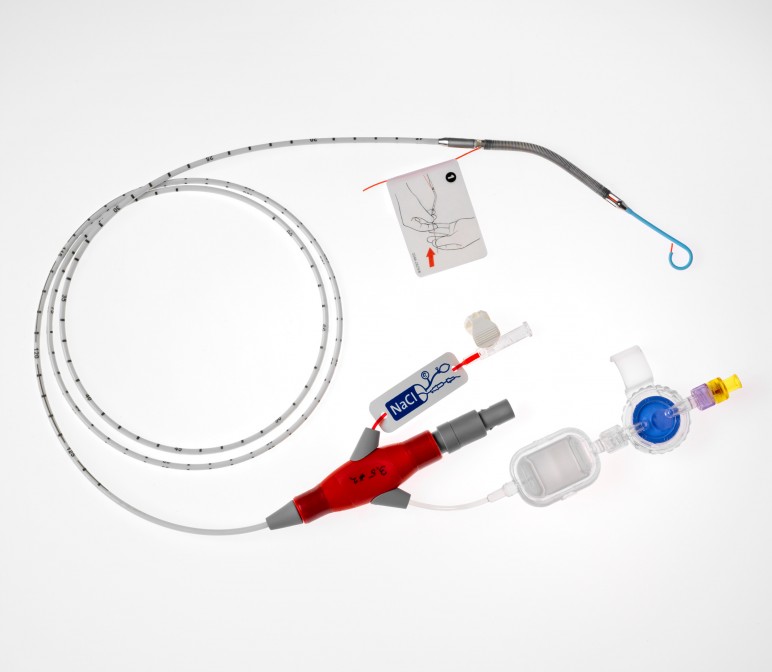
The University of Glasgow presented research at the British Cardiovascular Society's annual conference, yesterday that proves a pressure- and temperature-sensitive wire inserted into a coronary artery after a heart attack can predict heart failure.
The University of Glasgow presented research at the British Cardiovascular Society's annual conference, yesterday that proves a pressure- and temperature-sensitive wire inserted into a coronary artery after a heart attack can predict heart failure.
The standard assessment, a coronary angiogram, "can only identify narrowed vessels and cannot tell the doctor if, or how much, heart blood vessel damage has occurred," writes Medical News Today. Using the wire, the level of damage to arteries after a heart attack can be assessed in minutes -- a key indicator of high risk for heart failure.
The new assessment could lead to quicker treatment of patients at greatest risk for heart failure and improve outcomes.